Introduction to Combinations (\(^nC_r\)) in Visual Basic
Combinatorics is a key area of mathematics and computer science, and one of its most common applications is calculating combinations. In this tutorial, you'll learn how to implement a Visual Basic combination algorithm to calculate \(^nC_r\) in Visual Basic. We'll explore how to generate all possible selections without repetition, compare combinations with permutations, and walk through practical coding examples.
What Is a Combination? | Mathematics Explanation for Visual Basic Kids
A combination is a way of selecting items from a group where order does not matter. For example, choosing 3 students out of a class of 10 is a combination problem. In Visual Basic, we can write functions to calculate these selections efficiently.
A combination answers the question: “In how many different ways can r items be chosen from n items when order is irrelevant?” For example, choosing {A, B} is the same as choosing {B, A}. Because the order does not matter, combinations differ from permutations.
Combinations are commonly used in:
- Probability calculations
- Statistical analysis
- Algorithmic problem solving
- Data sampling and modeling
Understanding how combinations work mathematically makes it easier to implement them correctly in programming languages such as Visual Basic.
Combination Formula (\(^nC_r\)) Explained
The standard formula for combinations is written as \(^nC_r\) and defined as:
- n is the total number of items
- r is the number of items selected
- ! denotes factorial
This formula computes the number of possible selections without repetition and without regard to order.
Combinations vs. Permutations | Maths Explanation for Visual Basic Kids
It is easy to confuse these two concepts. Remember:
- Combination: Choosing a team of 3 students from a class of 20 (Order doesn't matter).
- Permutation: Assigning a President, VP, and Secretary from a class of 20 (Order matters).
This page is specifically designed for selection without repetition, the standard definition of the combination formula.
Selection Without Repetition Using Visual Basic
In selection without repetition, once an item is chosen, it cannot be chosen again. This assumption is built directly into the combination formula and is reflected in the Visual Basic implementation above.
This type of algorithm is commonly used when:
- Selecting unique samples from a dataset
- Solving probability problems
- Analyzing possible outcomes in simulations
- Teaching foundational combinatorics concepts
The Visual Basic function that follows computes the number of combinations for a given n and r. It correctly models selection without repetition and provides a clear illustration of how combinatorial math can be translated into code.
The example shown here emphasizes clarity and correctness, making it ideal for students learning both Visual Basic math algorithms and basic combinatorics.
Visual Basic Code for Computing Combinations
Writing up an algorithm in Visual Basic to carry out the different Combination - Selection without Repetition, nCr - of a set of things requires some level of imaginative thinking.
Get a writing pad and pencil:
- Write out all n members in the set - for Combination - at the top of the pad.
- Beginning with the first member, match it separately with the other members until the required selected-group size (r) is reached.
-
When every possible Combination for this first member is
exhausted, remove the current first member from the mother set.
The immediate next member becomes the new first member in the culminating set. - Take the first member in what is left of the mother set and repeat the same process from step II.
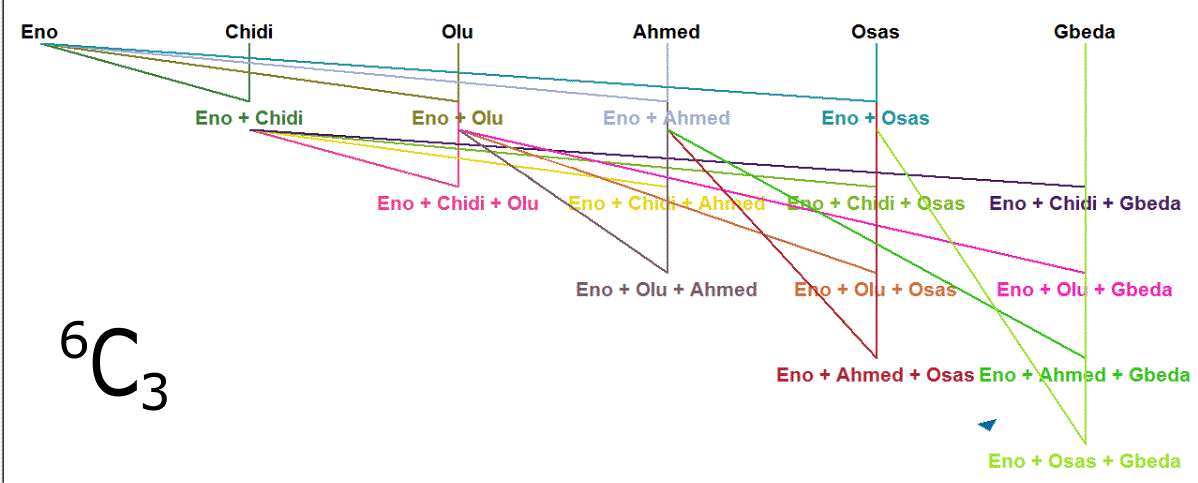
This is exactly what we will do with code to list up all
possible selections without repetition in VB.Net.
Create a new Visual Basic project;
call it Miscellaneous_VS
.
You can rename the module name -- just right-click on the name from the
Solution Explorer panel -- to Miscellaneous_Combination
if you want.
Create a new Visual Basic class file;
call it Combination
.
Type out the adjoining VB.Net algorithm for the combination of different options
(\(^nC_r\)).
Why Combinations Matter in Programming | Explanation for Visual Basic Kids
Combination algorithms play an important role in many real-world programming scenarios. They help developers:
- Calculate possible outcomes efficiently
- Model real-life probability situations
- Apply mathematical reasoning to software solutions
Learning how to compute combinations in Visual Basic bridges the gap between theoretical mathematics and practical programming, reinforcing both disciplines simultaneously.
Practical Applications | Explanation for Visual Basic Kids
- Student group selection
- Lottery number generation
- Word combinations in Visual Basic
- Algorithm practice problems for beginners
Summary: Visual Basic Combination Algorithm
By understanding and implementing the Visual Basic combination algorithm, you can solve a wide range of problems in mathematics and programming. Whether you're calculating \(^nC_r\) in Visual Basic, generating all possible selections, or comparing combination vs permutation in Visual Basic, these techniques are essential for developers and learners alike.
This tutorial demonstrated how to:
- Understand combinations and the \(^nC_r\) formula
- Apply combinatorics concepts in Visual Basic
- Implement a clear combination algorithm for selection without repetition
By mastering these ideas, learners gain a solid foundation in both mathematical reasoning and Visual Basic algorithm development.
VB.Net Code for Combination - Class File
Public words As New List(Of String)
Public r As Integer ' min length Of word
Protected comb_store As List(Of String())
Private i As Integer
' point of entry
Public Function possibleWordCombinations(candidates As List(Of String), size As Integer) As List(Of String())
words = candidates
r = size
comb_store = New List(Of String())
i = 0
' check for conformity
If r <= 0 Or r > words.Count Then
comb_store = New List(Of String())
ElseIf r = 1 Then
For i = 0 To words.Count - 1
comb_store.Add(New String() {words(i)})
Next i
Else
progressiveCombination()
End If
Return comb_store
End Function
' do combinations for all 'words' element
Private Sub progressiveCombination()
' single member list
repetitivePairing(New List(Of String)({words(i)}), i + 1)
If i + r <= words.Count Then
' move on to next degree
i += 1
progressiveCombination()
End If
End Sub
' do all possible combinations for 1st element of this array
Private Sub repetitivePairing(prefix As List(Of String), position As Integer)
Dim auxiliary_store(words.Count - position) As List(Of String)
For j As Integer = 0 To words.Count - position - 1
' check if desired -- r -- size will be realised
If r - prefix.Count <= words.Count - position Then
auxiliary_store(j) = New List(Of String)
auxiliary_store(j).AddRange(prefix)
auxiliary_store(j).Add(words(position))
If auxiliary_store(j).Count < r Then
' see to adding next word on
repetitivePairing(auxiliary_store(j), position + 1)
Else
comb_store.Add(auxiliary_store(j).ToArray())
End If
End If
position += 1
Next j
End Sub
End Class
VB.Net Code for Combination - Main Module
Sub Main()
Dim goods As List(Of String)
goods = New List(Of String)(New String() {"Eno", "Chidi", "Olu", "Ahmed", "Osas", "Gbeda"})
Dim combo As New Combination
Dim result As List(Of String()) = combo.possibleWordCombinations(goods, 3)
' print choices and operation
Console.Write("[ ")
For Each choice As String In combo.words
Console.Write(choice & "; ")
Next
Console.WriteLine("] combination " & combo.r & ":" & Environment.NewLine)
' print out combinations nicely
Dim i As Integer = 0
For Each group As String() In result
i += 1
Console.Write(i & ": ")
For Each member As String In group
Console.Write(member & "; ")
Next
Console.WriteLine()
Next
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine & "Number of ways is " & result.Count & ".")
End Sub
End Module
