Understanding Periodic Functions | Maths Explanation for Java Kids
In this tutorial, we'll learn how to use Java periodic functions to create animations of sine and cosine waves. Understanding periodic functions is an essential part of senior secondary mathematics, and Java offers a fun, visual way to explore them.
What Are Periodic Functions? | Maths Explanation for Java Kids
A periodic function repeats its values at regular intervals. Common examples include the sine and cosine functions. In mathematics, these functions are essential for modeling waves and oscillations. In Java, we can easily simulate periodic functions like the sine and cosine curves using simple trigonometric equations. We'll represent these functions graphically using Java Canvas.
Properties of Periodic Functions: Period, Amplitude & Frequency | Maths Explanation for Java Kids
Every periodic function has three key properties:
- Amplitude - the maximum height of the wave from its central position.
- Period - the horizontal distance over which the function repeats.
- Frequency - the number of complete cycles per unit interval.
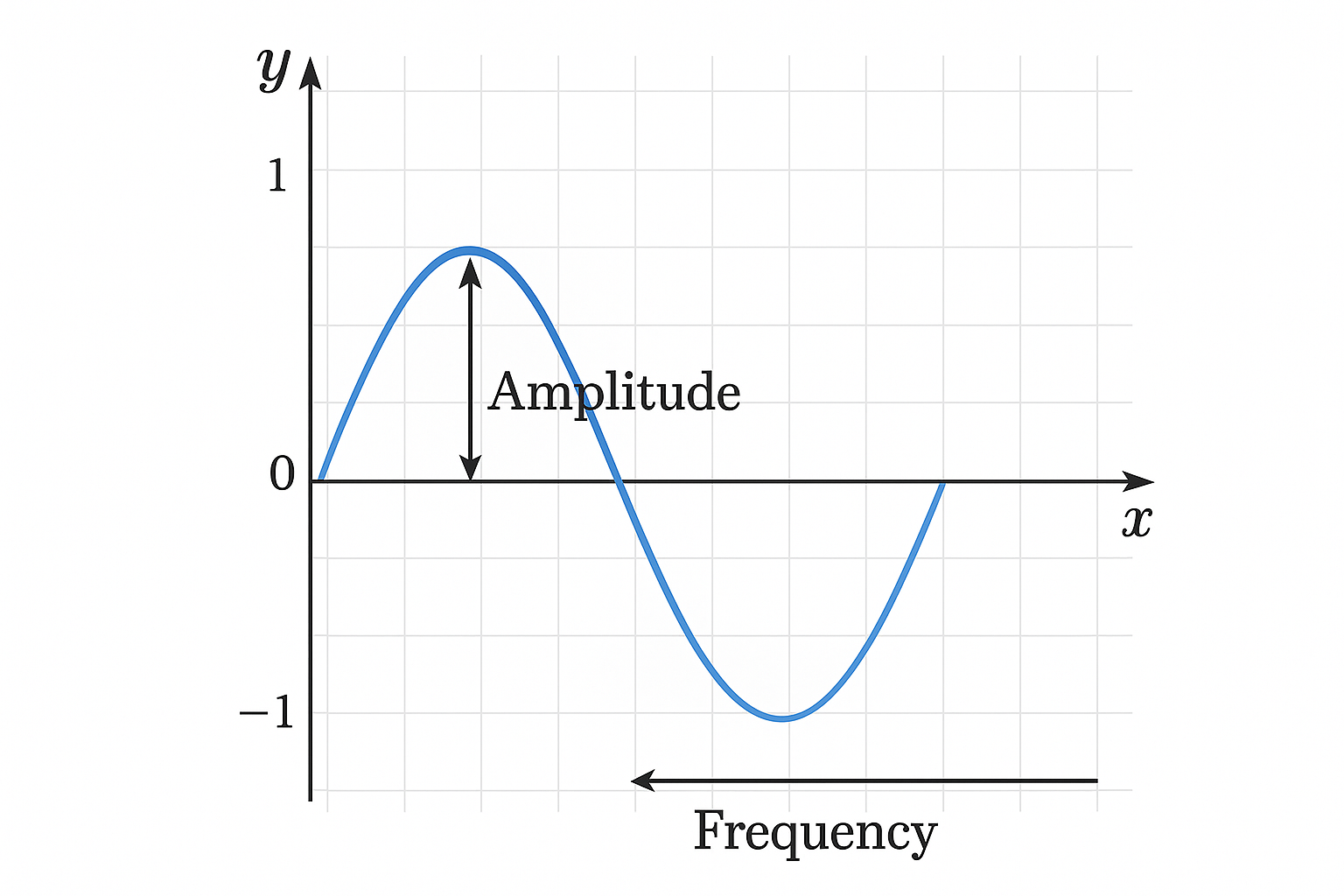
Understanding these properties helps in analyzing periodic function graphs and predicting their patterns.
How to Simulate Sinusoidal Curves in Java
Periodic functions produce an infinite order of sinusoidal curves.
The sine function has the general form
y = a × sin(θ) + c;
and the cosine function has the general form
y = a × cos(θ) + c;
where θ is angle in radians and
a is an arbitrary constant that heightens
the curve.
Animating a Periodic Wave Using Java
We can animate a sine or cosine wave in Java using the Java Canvas. By incrementing θ continuously and computing y using the trigonometric function, a dot or object moves along a periodic path that represents the wave. The angle θ is in radians, and you can use any c value that gives a satisfactory amplitude.
Create a new Java project;
call it Dymetric.
Create 3 new Java classes; File, New.
Call them Facet, PanelsPeriodicFunction and PeriodicFunction.
Type out the adjoining Java code for animating an image body through
the path of a sine / cosine curve.
This code draws one complete periodic sine wave, allowing students to observe how the function repeats its pattern.
Exploring the Cosine Function in Java
Similar to the sine wave, we can animate the cosine curve using Java trigonometric animation techniques.
Note: To create a cosine wave animation, simply replace Math.sin with Math.cos.
Key Takeaways on Periodic Wave Animation in Java
In this tutorial, you've learned:
- Periodic functions repeat after a fixed interval called the period
- They are fundamental in trigonometry, wave analysis, and Java visualizations.
- Use the Java graphing example to explore amplitude, period, and phase shift interactively.
By blending mathematics and coding, students can better visualize abstract periodic concepts and prepare for advanced studies in both fields.
FAQs: Periodic Functions and Java
What is a periodic function in Java?
A periodic function repeats its values over intervals, such as sine or cosine, and can be represented graphically using Java Canvas and trigonometric functions.
How do you animate a sine wave using Java?
Use the Math.sin() function with the Java Canvas to simulate oscillations.
Can I animate objects along a periodic path in Java?
Yes! You can use sine and cosine to calculate x and y positions for smooth, looping motion.
Applications of Periodic Functions in Java Programming and STEM Education
Periodic functions are used in physics, sound waves, and even game development. By coding these in Java, students can visualize maths periodic functions dynamically.
Understanding periodic functions in Java helps students visualize mathematical concepts such as oscillation, waves, and harmonic motion. These concepts apply in fields like physics, sound processing, and even game development, where trigonometric animation brings realism to motion.
Summary: Periodic vs Aperiodic Functions | Maths Explanation for Java Kids
Periodic functions in Java are useful for simulating waves, oscillations, and rhythmic motion. Understanding the period, amplitude, and frequency of these functions helps you create dynamic visuals, animations, and simulations. Whether you're studying math periodic functions or applying them in web development, these tools make complex periodic behavior easier to model and visualize.
Not every function repeats itself.
- A periodic function has a consistent cycle (e.g., sine, cosine).
- An aperiodic function does not repeat (e.g., linear or exponential functions).
Understanding this difference helps students see why periodic motion is predictable - an important skill in physics, sound, and electrical circuits.
Mastering periodic functions prepares students for advanced trigonometry and real-life applications such as sound waves and electrical signals. Practice with our periodic function examples and questions to strengthen your understanding.
So! Java Fun Practice Exercise - Animate along Periodic Wave
As a fun practice exercise, try modifying parameters like amplitude or frequency to explore how periodic functions in Java behave. You can also:
- Plot f(θ) = a * cos(θ) + c
- Plot f(θ) = a * sin(2θ) + c
- Write a Java function that combines sine and cosine
This will be a great way to connect mathematics and programming, and help you understand more about Java animations and periodic functions.
Java Periodic Wave Code - Main Class
public class Dymetric {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Facet lcd = new Facet();
lcd.setVisible(true);
}
}
Java Periodic Wave Window Setup - Facet Class
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* This class just creates a display window to attach our canvas to.
*/
public class Facet extends JFrame {
public Container face;
public ButtonandCanvasPanels components;
public ImageIcon logo;
public Facet() {
// Give our window a title
super("A window that will hold a Canvas and Button");
// set window start points and dimensions
setSize(780,400);
// close the window when told to
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setResizable(true); // should this window be resizable?
// It'll be nice to have our own logo (feel free to use yours)
logo = new ImageIcon(getClass().getResource("studyingPays.png"));
this.setIconImage(logo.getImage());
face = this.getContentPane();
// background colour - may not be necessay since our canvas will have a colour of its own
face.setBackground(Color.PINK);
components = new ButtonandCanvasPanels();
// using the default layout manager
face.add(components.button_panel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
// attach appropriate drawing component
face.add(components.canvas_panel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
}
Java Periodic Wave Canvas and Button Controls Class
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class ButtonandCanvasPanels implements ActionListener {
public JPanel button_panel, canvas_panel;
public JButton motion_bttn;
public PeriodicFunction pf_track;
public ButtonandCanvasPanels() {
button_panel = new JPanel();
// pick a background colour
button_panel.setBackground(Color.PINK);
button_panel.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER, 0, 0));
// O my; but for convenience sake let's add our control button here
motion_bttn = new JButton("Move");
motion_bttn.setBackground(new Color(255, 0, 255));
motion_bttn.addActionListener(this);
// using the default layout manager
button_panel.add(motion_bttn);
canvas_panel = new JPanel();
canvas_panel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
pf_track = new PeriodicFunction();
// attach appropriate drawing component
canvas_panel.add(pf_track, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
/**
* Respond to the button click event
*/
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
pf_track.moveSinusoidal();
}
}
Java Animation Code for Periodic Function Class
import java.awt.*;
public class PeriodicFunction extends Canvas {
protected Color ball_colour;
protected int theta = 0;
protected int a = 100; // constant
protected int y;
protected final int aWIDTH, aHEIGHT;
public PeriodicFunction() {
setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY); // canvas color
ball_colour = Color.RED;
aWIDTH = aHEIGHT = 10;
// convert theta from degree to radians
y = (int) Math.round(a * Math.sin(theta * (double) Math.PI / 180));
}
// Feel free to double buffer if flickering occurs
public void paint(Graphics g) {
g.translate(0, 150);
g.setColor(ball_colour);
// draw a dot
g.fillOval(theta, y, aWIDTH, aHEIGHT);
}
public void moveSinusoidal() {
// condition for continuing motion
while (theta < 750) {
y = (int) Math.round(a * Math.sin(theta * (double) Math.PI / 180));
paint(this.getGraphics());
theta += 15;
// introduce a delay between renderings
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
}
